Desde teléfonos inteligentes hasta computadoras, desde dispositivos domésticos inteligentes hasta sistemas de control de automatización industrial, el rendimiento y la confiabilidad de los productos electrónicos se someten a un intenso escrutinio. Sin embargo, a lo largo de su ciclo de vida, estos productos inevitablemente se enfrentan a diversas condiciones climáticas, como altas y bajas temperaturas, alta humedad y fluctuaciones de temperatura y humedad. Estos factores ambientales pueden afectar gravemente el rendimiento, la vida útil y la confiabilidad de los productos electrónicos, e incluso provocar fallas.
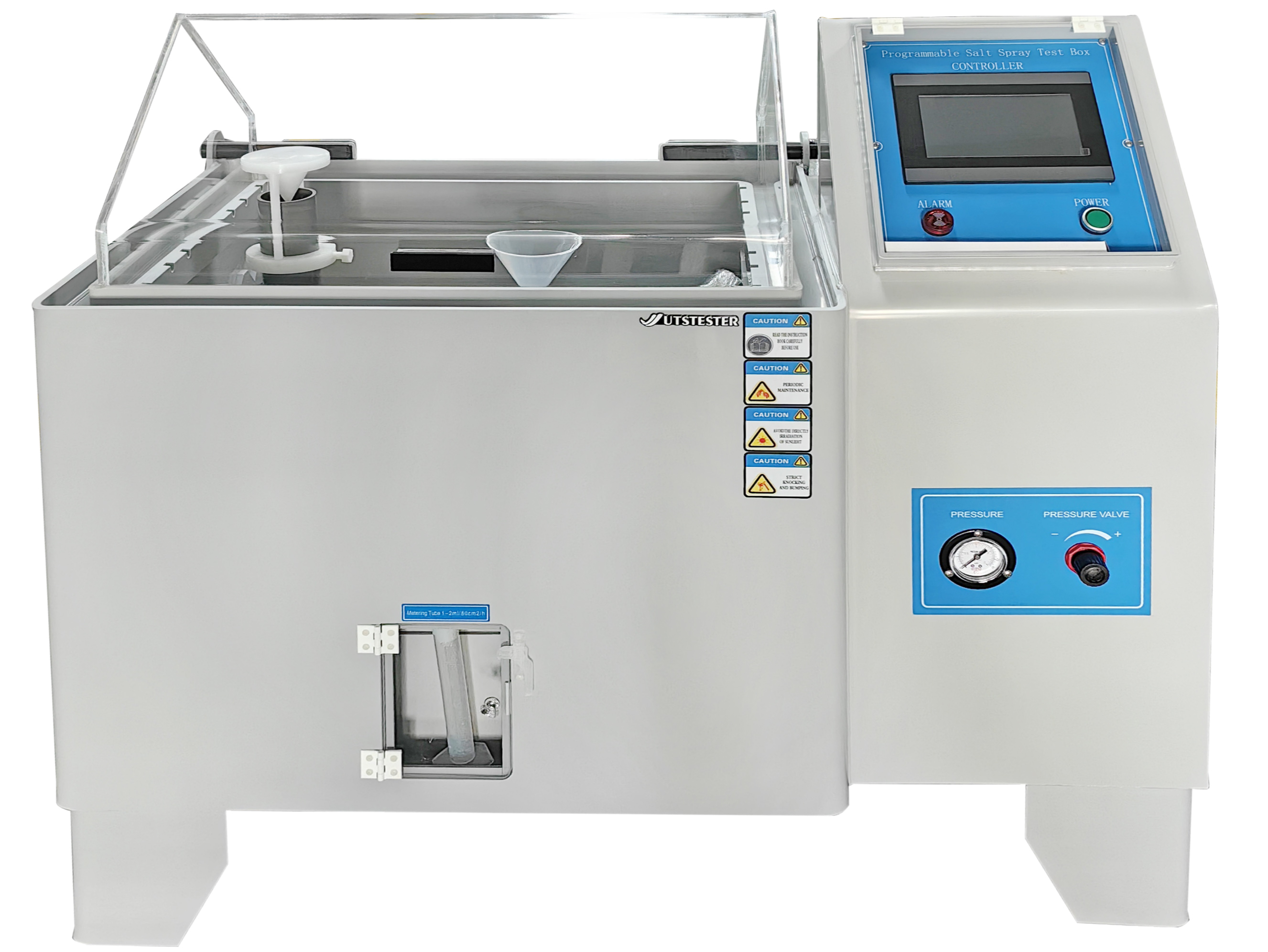
Cámaras de pruebas ambientales
servir como equipo central para abordar este desafío y fortalecer las defensas de la calidad del producto.
Los entornos operativos de los productos y materiales electrónicos son complejos y variables: desde condiciones tropicales de alta temperatura y alta humedad hasta regiones frías con bajas temperaturas, desde la corrosión por niebla salina costera hasta choques térmicos durante el transporte. Cualquier condición extrema puede provocar fallos de rendimiento. Las pruebas convencionales solo pueden verificar el rendimiento del producto en condiciones estándar, sin predecir los riesgos potenciales en el uso real. Las cámaras de pruebas ambientales simulan artificialmente estos entornos complejos, condensando meses o incluso años de envejecimiento natural en días o semanas, completando así la verificación de fiabilidad con antelación.
I. Pruebas ambientales básicas para electrónica
Ciclos de temperatura
El ciclo de temperatura examina la respuesta del equipo a cambios repetidos entre condiciones de calor y frío. Identifica eficazmente grietas en las soldaduras, fallos en los sellos y problemas de expansión del material. Las cámaras con control preciso de temperatura garantizan la repetibilidad y trazabilidad de cada ciclo.
Prueba de humedad
La humedad afecta los circuitos internos, los materiales y los adhesivos. Las pruebas con alta humedad revelan signos tempranos de corrosión o penetración de humedad. Las cámaras Cantrol se especializan en el control constante de la humedad para facilitar estas pruebas.
Las cámaras estables mantienen condiciones ambientales constantes, lo que permite ciclos de prueba prolongados, especialmente cuando los productos requieren una exposición prolongada a altas temperaturas o humedad.
Cámara de temperatura y humedad constantes
para pruebas de productos
Choque térmico
El choque térmico somete a los equipos a fluctuaciones rápidas entre calor y frío extremos. Esta prueba simula eventos reales, como el paso de un ambiente interior a un ambiente exterior frío. Los resultados muestran la resistencia de los materiales a las tensiones causadas por la expansión y contracción repentinas.
Vibración y choque
Las pruebas de vibración mecánica examinan la resistencia de los dispositivos electrónicos durante el transporte, el funcionamiento o el uso prolongado. Las pruebas de impacto simulan impactos como caídas accidentales o colisiones de dispositivos. Estas pruebas ayudan a confirmar la estabilidad mecánica.
Prueba de altitud
Las cámaras de altitud simulan entornos de baja presión durante el transporte aéreo o las operaciones a gran altitud. Estas pruebas son especialmente valiosas para productos que contienen baterías o carcasas selladas.
Pruebas de polvo y entrada
Ciertos dispositivos electrónicos requieren resistencia al polvo o protección general. Las pruebas de polvo garantizan que las partículas no penetren en zonas sensibles. Los resultados ayudan a las empresas a obtener la clasificación IP cuando es necesario.
II. Tipos de cámaras de pruebas ambientales convencionales y escenarios de aplicación
1. Tipo de entorno climático (niebla salina, humedad/calor, temperatura alta/baja): simula condiciones climáticas como temperatura/humedad, niebla salina y radiación UV para probar la resistencia a la corrosión del material y el rendimiento frente al envejecimiento.
Escenarios de aplicación típicos: equipos electrónicos costeros, terminales de comunicación al aire libre, carcasas de material polimérico
2. Tipo de entorno mecánico (vibración, choque, caída): simula tensiones mecánicas como vibración, impactos transitorios y caídas libres para validar la resistencia estructural y la confiabilidad de la conexión de los componentes.
Aplicaciones típicas: Electrónica automotriz, electrónica de consumo, componentes aeroespaciales.
3. Pruebas ambientales combinadas (triple combinación, temperatura y niebla salina combinadas):
Simulación coordinada de múltiples factores para replicar tensiones ambientales complejas encontradas en escenarios del mundo real.
Aplicaciones típicas: Electrónica naval, semiconductores de alta gama, nuevos equipos de energía.
III. La importancia de las pruebas en cámaras climáticas en productos electrónicos
(A) Simulación de entornos extremos y del mundo real
1. Simulación de entornos de alta temperatura y su impacto en los productos electrónicos
En entornos de alta temperatura, los componentes electrónicos de los productos se enfrentan a graves desafíos. Por ejemplo, el rendimiento de los dispositivos semiconductores puede variar con el aumento de la temperatura, lo que provoca la inestabilidad de los parámetros del circuito. El calor excesivo también acelera el envejecimiento de los componentes, acortando su vida útil. Tomemos como ejemplo las CPU de los ordenadores: el funcionamiento prolongado a altas temperaturas puede provocar una disipación térmica inadecuada, activando la limitación automática para proteger el chip y reduciendo significativamente el rendimiento del sistema. En casos graves, esto puede incluso causar daños permanentes a la CPU.
2. Simulación de entornos de baja temperatura y consecuencias
Las bajas temperaturas también suponen un reto para los productos electrónicos. Ciertos materiales se vuelven frágiles con el frío; las carcasas de plástico pueden agrietarse, lo que compromete la estética y la integridad de la protección del producto. En el caso de los dispositivos electrónicos que funcionan con batería, las bajas temperaturas reducen significativamente la actividad de la batería y acortan su vida útil. Por ejemplo, la duración de la batería de los smartphones suele disminuir notablemente durante los inviernos fríos, lo que ilustra el impacto directo de las bajas temperaturas en el rendimiento de la batería.
3. Desafíos en entornos de alta humedad
La humedad alta es uno de los mayores enemigos de los productos electrónicos. La humedad puede formar vías conductoras en las placas de circuitos, provocando cortocircuitos y fallos repentinos. Simultáneamente, la humedad alta acelera la corrosión de componentes metálicos como conectores y cables dentro de los dispositivos electrónicos. La corrosión aumenta la resistencia de contacto, degrada la calidad de la transmisión de la señal y, en última instancia, provoca un menor rendimiento o fallos del producto.
4. Prueba de la estructura y funcionalidad del producto bajo temperatura y humedad
En la práctica, los productos electrónicos se enfrentan frecuentemente a condiciones de temperatura y humedad variables, como la transición de ambientes exteriores fríos a espacios interiores cálidos y húmedos. Estos rápidos cambios de temperatura y humedad inducen tensiones de expansión y contracción térmica dentro del producto, lo que pone en peligro su integridad estructural. Por ejemplo, en dispositivos electrónicos mal sellados, la humedad puede filtrarse durante estos ciclos, dañando los componentes internos o causando problemas graves como la delaminación de la placa de circuito debido a la exposición repetida.
(2) Prueba de la confiabilidad y estabilidad del producto
1. Pruebas de exposición a largo plazo para determinar la vida útil y la durabilidad del producto
El ciclo de vida de los productos electrónicos en uso real puede aproximarse mediante pruebas de exposición ambiental simulada prolongada en cámaras climáticas. Por ejemplo, colocar un lote de productos electrónicos en un
cámara climática
La configuración en condiciones de alta temperatura y alta humedad durante varios meses permite observar cambios en las métricas de rendimiento (como tasas de fallas o tasas de degradación del rendimiento), lo que proporciona una base científica para establecer el período de garantía y evaluar la confiabilidad.
2. Pruebas cíclicas para evaluar la adaptabilidad en transiciones ambientales
Las pruebas de ciclos de temperatura y humedad evalúan eficazmente la adaptabilidad de un producto electrónico durante cambios frecuentes entre diferentes condiciones ambientales. Por ejemplo, ciertos dispositivos electrónicos de exterior deben funcionar de forma estable en condiciones de altas temperaturas diurnas, bajas temperaturas nocturnas y fluctuaciones significativas de humedad. Al simular estos ciclos de temperatura y humedad en una cámara climática y observar los cambios de rendimiento tras varios ciclos (por ejemplo, si el producto arranca con normalidad o mantiene su funcionalidad completa), se puede determinar la adaptabilidad y la fiabilidad del producto.
Conclusión
Ya sea en la electrónica de consumo, la automoción, las nuevas energías u otros sectores civiles, o en la industria aeroespacial, la defensa y otros campos de fabricación de alta gama, las cámaras de pruebas ambientales se han convertido en el soporte fundamental para las pruebas de fiabilidad de los productos. Sirven no solo como "detectores" para identificar defectos, sino también como "pasaportes" para la certificación de conformidad y "optimizadores" para el control de costes. En medio de la tendencia de la industria hacia un desarrollo de alta calidad, las pruebas de simulación ambiental precisas son la vía esencial para que los productos y materiales electrónicos se consoliden en el mercado y generen confianza.

Correo electrónico:
hello@utstesters.com
Directo: + 86 152 6060 5085
Teléfono: +86-596-7686689
Web:
www.utstesters.com
 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085




 English
English русский
русский español
español português
português









 hello@utstesters.com
hello@utstesters.com hello@utstesters.com
hello@utstesters.com +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085 +8615260605085
+8615260605085