Textiles (such as clothing, furniture fabrics, bedding, etc.) may come into contact with fire sources (such as open flames, high-temperature electrical appliances, cigarettes, etc.) during daily use. Their combustion characteristics are directly related to fire risk and personal safety. Therefore, imparting flame-retardant properties to textiles is of great significance in eliminating fire hazards, preventing the spread of fire, and reducing loss of life and property.
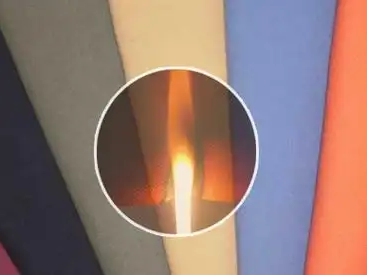
1. Vertical burning method: Mainly used for flame retardancy testing of clothing textiles, curtains, and other fabrics. This testing method requires the test sample to be placed vertically (with the length direction of the test sample perpendicular to the horizontal line). The ignition source is located below the test sample to initiate combustion. Key indicators related to flame-retardant performance include the minimum ignition time, sustained burning time, smoldering time, flame spread rate, char length (damaged length), and char area (damaged area) of the test sample.
Normas de prueba comunes para el método de combustión vertical:
GB/T5455 Método de prueba para inflamabilidad de textiles;
GB/T8745 Determinación de la longitud del daño vertical, resistencia a la llama y tiempo de combustión sostenida de textiles;
16CFR1615/1616 Prueba de inflamabilidad para ropa de dormir para niños.
2. Método de combustión de 45°: este método de prueba especifica que la muestra de prueba se coloca en un ángulo de 45° (con la longitud de la muestra de prueba formando un ángulo de 45° con la línea horizontal) y mide el tiempo necesario para que la muestra se queme hacia arriba sobre una cierta distancia, o mide el tiempo de combustión posterior a la llama, el tiempo de combustión lenta, la velocidad de propagación de la llama, la longitud de la combustión, el área de combustión o la cantidad de veces que la muestra debe entrar en contacto con la llama para quemarse hasta una cierta distancia debajo de la muestra, entre otros indicadores relacionados con el rendimiento retardante de llama.
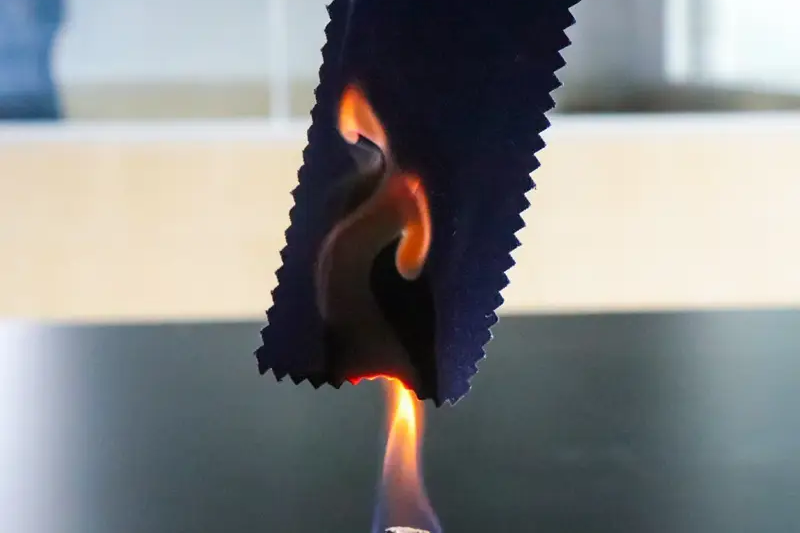

Normas de prueba comunes para el método de combustión a 45°:
GB/T14644 Determinación de la velocidad de combustión en la dirección de 45° para el rendimiento de combustión de textiles;
ASTM D1230 Método de prueba estándar para inflamabilidad de textiles de prendas de vestir;
16 CFR PARTE 1610 Norma de prueba de inflamabilidad para textiles de indumentaria;
CAN/CGSB-4.2 No. 27.5 Rendimiento de combustión de llama a 45° de textiles canadienses.
3. Método de Combustión Horizontal: Se utiliza principalmente para comprobar la inflamabilidad de sacos de dormir y mantas infantiles. Este método de prueba consiste en exponer la superficie de la muestra a una llama estandarizada durante un periodo de tiempo específico, observar la velocidad de combustión, la extensión del daño o el cambio de color de la muestra y, posteriormente, clasificar la tela analizada.
Normas de prueba comunes para el método de combustión horizontal:
Prueba de inflamabilidad de sacos de dormir para niños CPAI75
Método de prueba de inflamabilidad de sacos de dormir ASTM F1955
Método de prueba de inflamabilidad de manta ASTM D4151

Correo electrónico:
hello@utstesters.com
Directo: + 86 152 6060 5085
Teléfono: +86-596-7686689
Web:
www.utstesters.com
 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085




 English
English русский
русский español
español português
português











 hello@utstesters.com
hello@utstesters.com hello@utstesters.com
hello@utstesters.com +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085 +8615260605085
+8615260605085